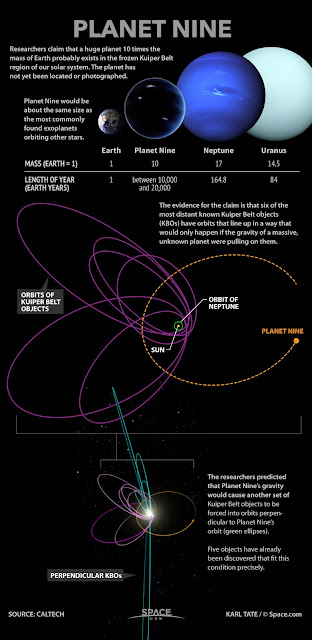
The red supergiant 22 million light years from Earth known as N6946-BH1attracted attention in a 2009 survey for failed supernova using the Large Binocular Telescope in Arizona.
The star brightened over the course of several months before visibly fading from view six years later, falling well short of blasting into the expected light-show called a supernova.
There are two types of supernova:
- Type I follows events where a star's gravity pulls material in from a neighbour until the star collapses in on itself in a rush.
- Type II describes the death of a star that has about 8 to 15 times the amount of mass as our Sun, which has collapses once it has used up its fuel and can't produce enough heat to overcome its own gravitational squeezing.
In both cases the crunch of material being squeezed together is enough to produce a spectacular blast of radiation as the collapsing gases push back from a dense core.
But not all star deaths live up to our expectations, it seems. Given all the big stars out there, we seem to be short on supernovae.
N6946-BH1 had a mass 25 times that of our own Sun, putting it well above a limit considered big enough to undergo a Type II supernova, and in a zone astronomers would expect a black hole to form from its remains.
So a team of American researchers from the Ohio State University took a closer look at the supergiant's remains using the Hubble Space Telescope, and compared the results from the survey with other observations from around the world.
Sure enough, the star brightened between March and May in 2009 and then faded from optical view, continuing to shine in slowly dimming infra-red light.
Before jumping to conclusions, the team ruled out whether dust might have hidden the potential supernova from view.
"The gist is that no models using dust to hide the star really work, so it would seem that whatever is there now has to be much less luminous then that pre-existing star," lead researcher Christopher Kochanek from Ohio State said last year.
So it seems the star really did fizzle out, and no supernova happened. The question that remained was what happened to it? Could it still have produced a black hole?
"Within the context of the failed supernova model, the residual light is consistent with the late time decay of emission from material accreting onto the newly formed black hole," said Kochanek.
In simpler terms, for a black hole to form in spite of the supernova's failure, there would need to be another process going on.
Picture the red supergiant as hydrogen expanding out to something the size of Jupiter's orbit, with a dense core of elements the size of Earth that's barely holding onto this hot atmosphere.
When the core collapses in this case, it loses a fraction of its mass in the form of tiny particles called neutrinos, and produces a shock wave that pushes away its cloud of hydrogen.
Compared to a supernova, what's left behind is pretty low-key. The surrounding cloud expands and cools, so electrons that had been ripped away from the hydrogen re-join the atoms, slowly releasing energy to contribute to the black hole's formation.
Which seems to be what happened to N6946-BH1.
"The typical view is that a star can form a black hole only after it goes supernova," Kochanek explained recently.
"If a star can fall short of a supernova and still make a black hole, that would help to explain why we don't see supernovae from the most massive stars."
It's not clear how many massive stars blink out rather than pop, but Scott Adams, an Ohio State student who earned his PhD on the study, suggested it could be as high as nearly a third.
"N6946-BH1 is the only likely failed supernova that we found in the first seven years of our survey. During this period, six normal supernovae have occurred within the galaxies we've been monitoring, suggesting that 10 to 30 percent of massive stars die as failed supernovae," Adams said.
What's a failure for a supernova is a win for astronomers; with new technologies emerging that allow us to study massive cosmological phenomena in the form of gravitational wave detectors, every new discovery will help us get closer to the bottom of some of our Universe's darkest holes.
For more details on this disappearing star, check out the clip below.
Source: sciencealert.com